Build a User Management App with Next.js
This tutorial demonstrates how to build a basic user management app. The app authenticates and identifies the user, stores their profile information in the database, and allows the user to log in, update their profile details, and upload a profile photo. The app uses:
- Supabase Database - a Postgres database for storing your user data and Row Level Security so data is protected and users can only access their own information.
- Supabase Auth - allow users to sign up and log in.
- Supabase Storage - allow users to upload a profile photo.
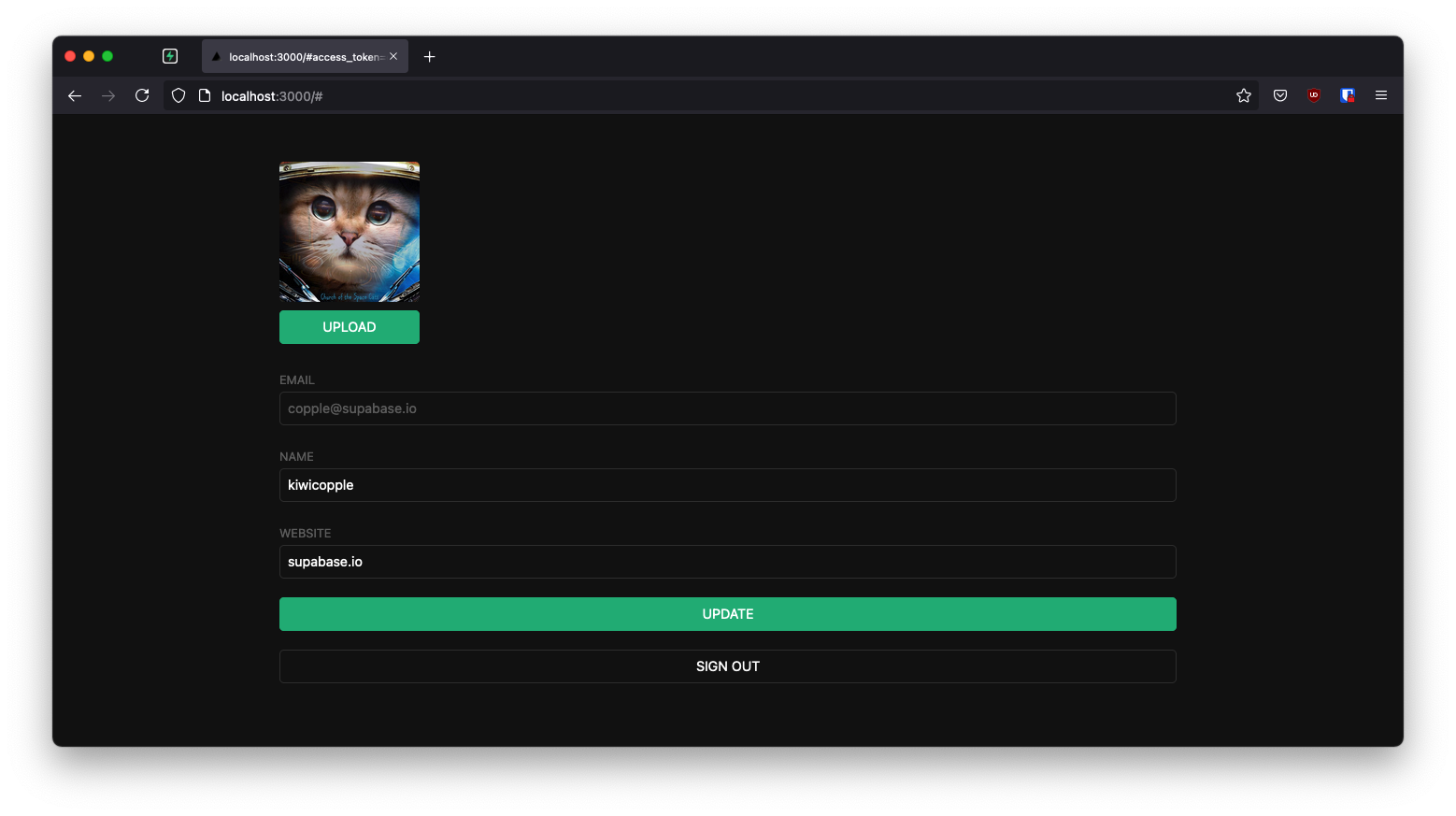
If you get stuck while working through this guide, refer to the full example on GitHub.
Project setup
Before you start building you need to set up the Database and API. You can do this by starting a new Project in Supabase and then creating a "schema" inside the database.
Create a project
- Create a new project in the Supabase Dashboard.
- Enter your project details.
- Wait for the new database to launch.
Set up the database schema
Now set up the database schema. You can use the "User Management Starter" quickstart in the SQL Editor, or you can copy/paste the SQL from below and run it.
- Go to the SQL Editor page in the Dashboard.
- Click User Management Starter under the Community > Quickstarts tab.
- Click Run.
You can pull the database schema down to your local project by running the db pull command. Read the local development docs for detailed instructions.
123supabase link --project-ref <project-id># You can get <project-id> from your project's dashboard URL: https://supabase.com/dashboard/project/<project-id>supabase db pullGet the API keys
Now that you've created some database tables, you are ready to insert data using the auto-generated API.
To do this, you need to get the Project URL and anon key from the API settings.
- Go to the API Settings page in the Dashboard.
- Find your Project
URL,anon, andservice_rolekeys on this page.
Building the app
Start building the Next.js app from scratch.
Initialize a Next.js app
Use create-next-app to initialize an app called supabase-nextjs:
12npx create-next-app@latest --use-npm supabase-nextjscd supabase-nextjsThen install the Supabase client library: supabase-js
1npm install @supabase/supabase-jsSave the environment variables in a .env.local file at the root of the project, and paste the API URL and the anon key that you copied earlier.
12NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_URL=YOUR_SUPABASE_URLNEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_ANON_KEY=YOUR_SUPABASE_ANON_KEYApp styling (optional)
An optional step is to update the CSS file app/globals.css to make the app look nice.
You can find the full contents of this file in the example repository.
Supabase Server-Side Auth
Next.js is a highly versatile framework offering pre-rendering at build time (SSG), server-side rendering at request time (SSR), API routes, and middleware edge-functions.
To better integrate with the framework, we've created the @supabase/ssr package for Server-Side Auth. It has all the functionalities to quickly configure your Supabase project to use cookies for storing user sessions. Read the Next.js Server-Side Auth guide for more information.
Install the package for Next.js.
1npm install @supabase/ssrSupabase utilities
There are two different types of clients in Supabase:
- Client Component client - To access Supabase from Client Components, which run in the browser.
- Server Component client - To access Supabase from Server Components, Server Actions, and Route Handlers, which run only on the server.
It is recommended to create the following essential utilities files for creating clients, and organize them within utils/supabase at the root of the project.
Create a client.js and a server.js with the following functionalities for client-side Supabase and server-side Supabase, respectively.
123456789import { createBrowserClient } from '@supabase/ssr'export function createClient() { // Create a supabase client on the browser with project's credentials return createBrowserClient( process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_URL, process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_ANON_KEY )}Next.js middleware
Since Server Components can't write cookies, you need middleware to refresh expired Auth tokens and store them. This is accomplished by:
- Refreshing the Auth token with the call to
supabase.auth.getUser. - Passing the refreshed Auth token to Server Components through
request.cookies.set, so they don't attempt to refresh the same token themselves. - Passing the refreshed Auth token to the browser, so it replaces the old token. This is done with
response.cookies.set.
You could also add a matcher, so that the middleware only runs on routes that access Supabase. For more information, read the Next.js matcher documentation.
Be careful when protecting pages. The server gets the user session from the cookies, which anyone can spoof.
Always use supabase.auth.getUser() to protect pages and user data.
Never trust supabase.auth.getSession() inside server code such as middleware. It isn't guaranteed to revalidate the Auth token.
It's safe to trust getUser() because it sends a request to the Supabase Auth server every time to revalidate the Auth token.
Create a middleware.js file at the project root and another one within the utils/supabase folder. The utils/supabase file contains the logic for updating the session. This is used by the middleware.js file, which is a Next.js convention.
12345678910111213141516171819import { updateSession } from '@/utils/supabase/middleware'export async function middleware(request) { // update user's auth session return await updateSession(request)}export const config = { matcher: [ /* * Match all request paths except for the ones starting with: * - _next/static (static files) * - _next/image (image optimization files) * - favicon.ico (favicon file) * Feel free to modify this pattern to include more paths. */ '/((?!_next/static|_next/image|favicon.ico|.*\\.(?:svg|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|webp)$).*)', ],}Set up a login page
Login and signup form
Create a login/signup page for your application:
Create a new folder named login, containing a page.jsx file with a login/signup form.
1234567891011121314import { login, signup } from './actions'export default function LoginPage() { return ( <form> <label htmlFor="email">Email:</label> <input id="email" name="email" type="email" required /> <label htmlFor="password">Password:</label> <input id="password" name="password" type="password" required /> <button formAction={login}>Log in</button> <button formAction={signup}>Sign up</button> </form> )}Next, you need to create the login/signup actions to hook up the form to the function. Which does the following:
- Retrieve the user's information.
- Send that information to Supabase as a signup request, which in turns sends a confirmation email.
- Handle any error that arises.
The cookies method is called before any calls to Supabase, which takes fetch calls out of Next.js's caching. This is important for authenticated data fetches, to ensure that users get access only to their own data.
Read the Next.js docs to learn more about opting out of data caching.
Create the action.js file in the app/login folder, which contains the login and signup functions and the error/page.jsx file, and displays an error message if the login or signup fails.
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142'use server'import { revalidatePath } from 'next/cache'import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'import { createClient } from '@/utils/supabase/server'export async function login(formData) { const supabase = await createClient() // type-casting here for convenience // in practice, you should validate your inputs const data = { email: formData.get('email'), password: formData.get('password'), } const { error } = await supabase.auth.signInWithPassword(data) if (error) { redirect('/error') } revalidatePath('/', 'layout')}export async function signup(formData) { const supabase = await createClient() const data = { email: formData.get('email'), password: formData.get('password'), } const { error } = await supabase.auth.signUp(data) if (error) { redirect('/error') } revalidatePath('/', 'layout')}Email template
Before proceeding, change the email template to support support a server-side authentication flow that sends a token hash:
- Go to the Auth templates page in your dashboard.
- Select the Confirm signup template.
- Change
{{ .ConfirmationURL }}to{{ .SiteURL }}/auth/confirm?token_hash={{ .TokenHash }}&type=email.
Did you know? You can also customize other emails sent out to new users, including the email's looks, content, and query parameters. Check out the settings of your project.
Confirmation endpoint
As you are working in a server-side rendering (SSR) environment, you need to create a server endpoint responsible for exchanging the token_hash for a session.
The code performs the following steps:
- Retrieves the code sent back from the Supabase Auth server using the
token_hashquery parameter. - Exchanges this code for a session, which you store in your chosen storage mechanism (in this case, cookies).
- Finally, redirects the user to the
accountpage.
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233import { NextResponse } from 'next/server'import { createClient } from '@/utils/supabase/server'// Creating a handler to a GET request to route /auth/confirmexport async function GET(request) { const { searchParams } = new URL(request.url) const token_hash = searchParams.get('token_hash') const type = searchParams.get('type') const next = '/account' // Create redirect link without the secret token const redirectTo = request.nextUrl.clone() redirectTo.pathname = next redirectTo.searchParams.delete('token_hash') redirectTo.searchParams.delete('type') if (token_hash && type) { const supabase = await createClient() const { error } = await supabase.auth.verifyOtp({ type, token_hash, }) if (!error) { redirectTo.searchParams.delete('next') return NextResponse.redirect(redirectTo) } } // return the user to an error page with some instructions redirectTo.pathname = '/error' return NextResponse.redirect(redirectTo)}Account page
After a user signs in, allow them to edit their profile details and manage their account.
Create a new component for that called AccountForm within the app/account folder.
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899100101102103104105106107108109110111112113114115'use client'import { useCallback, useEffect, useState } from 'react'import { createClient } from '@/utils/supabase/client'export default function AccountForm({ user }) { const supabase = createClient() const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true) const [fullname, setFullname] = useState(null) const [username, setUsername] = useState(null) const [website, setWebsite] = useState(null) const getProfile = useCallback(async () => { try { setLoading(true) const { data, error, status } = await supabase .from('profiles') .select(`full_name, username, website, avatar_url`) .eq('id', user?.id) .single() if (error && status !== 406) { throw error } if (data) { setFullname(data.full_name) setUsername(data.username) setWebsite(data.website) } } catch (error) { alert('Error loading user data!') } finally { setLoading(false) } }, [user, supabase]) useEffect(() => { getProfile() }, [user, getProfile]) async function updateProfile({ username, website, avatar_url }) { try { setLoading(true) const { error } = await supabase.from('profiles').upsert({ id: user?.id, full_name: fullname, username, website, updated_at: new Date().toISOString(), }) if (error) throw error alert('Profile updated!') } catch (error) { alert('Error updating the data!') } finally { setLoading(false) } } return ( <div className="form-widget"> <div> <label htmlFor="email">Email</label> <input id="email" type="text" value={user?.email} disabled /> </div> <div> <label htmlFor="fullName">Full Name</label> <input id="fullName" type="text" value={fullname || ''} onChange={(e) => setFullname(e.target.value)} /> </div> <div> <label htmlFor="username">Username</label> <input id="username" type="text" value={username || ''} onChange={(e) => setUsername(e.target.value)} /> </div> <div> <label htmlFor="website">Website</label> <input id="website" type="url" value={website || ''} onChange={(e) => setWebsite(e.target.value)} /> </div> <div> <button className="button primary block" onClick={() => updateProfile({ fullname, username, website })} disabled={loading} > {loading ? 'Loading ...' : 'Update'} </button> </div> <div> <form action="/auth/signout" method="post"> <button className="button block" type="submit"> Sign out </button> </form> </div> </div> )}Create an account page for the AccountForm component you just created
123456789101112import AccountForm from './account-form'import { createClient } from '@/utils/supabase/server'export default async function Account() { const supabase = await createClient() const { data: { user }, } = await supabase.auth.getUser() return <AccountForm user={user} />}Sign out
Create a route handler to handle the sign out from the server side, making sure to check if the user is logged in first.
123456789101112131415161718192021import { createClient } from '@/utils/supabase/server'import { revalidatePath } from 'next/cache'import { NextResponse } from 'next/server'export async function POST(req) { const supabase = await createClient() // Check if a user's logged in const { data: { user }, } = await supabase.auth.getUser() if (user) { await supabase.auth.signOut() } revalidatePath('/', 'layout') return NextResponse.redirect(new URL('/login', req.url), { status: 302, })}Launch!
Now you have all the pages, route handlers, and components in place, run the following in a terminal window:
1npm run devAnd then open the browser to localhost:3000/login and you should see the completed app.
When you enter your email and password, you will receive an email with the title Confirm Your Signup. Congrats 🎉!!!
Bonus: Profile photos
Every Supabase project is configured with Storage for managing large files like photos and videos.
Create an upload widget
Create an avatar widget for the user so that they can upload a profile photo. Start by creating a new component:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687'use client'import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react'import { createClient } from '@/utils/supabase/client'import Image from 'next/image'export default function Avatar({ uid, url, size, onUpload }) { const supabase = createClient() const [avatarUrl, setAvatarUrl] = useState(url) const [uploading, setUploading] = useState(false) useEffect(() => { async function downloadImage(path) { try { const { data, error } = await supabase.storage.from('avatars').download(path) if (error) { throw error } const url = URL.createObjectURL(data) setAvatarUrl(url) } catch (error) { console.log('Error downloading image: ', error) } } if (url) downloadImage(url) }, [url, supabase]) const uploadAvatar = async (event) => { try { setUploading(true) if (!event.target.files || event.target.files.length === 0) { throw new Error('You must select an image to upload.') } const file = event.target.files[0] const fileExt = file.name.split('.').pop() const filePath = `${uid}-${Math.random()}.${fileExt}` const { error: uploadError } = await supabase.storage.from('avatars').upload(filePath, file) if (uploadError) { throw uploadError } onUpload(filePath) } catch (error) { alert('Error uploading avatar!') } finally { setUploading(false) } } return ( <div> {avatarUrl ? ( <Image width={size} height={size} src={avatarUrl} alt="Avatar" className="avatar image" style={{ height: size, width: size }} /> ) : ( <div className="avatar no-image" style={{ height: size, width: size }} /> )} <div style={{ width: size }}> <label className="button primary block" htmlFor="single"> {uploading ? 'Uploading ...' : 'Upload'} </label> <input style={{ visibility: 'hidden', position: 'absolute', }} type="file" id="single" accept="image/*" onChange={uploadAvatar} disabled={uploading} /> </div> </div> )}Add the new widget
Then add the widget to the AccountForm component:
1234567891011121314151617181920// Import the new componentimport Avatar from './avatar'// ...return ( <div className="form-widget"> {/* Add to the body */} <Avatar uid={user?.id} url={avatar_url} size={150} onUpload={(url) => { setAvatarUrl(url) updateProfile({ fullname, username, website, avatar_url: url }) }} /> {/* ... */} </div>)At this stage you have a fully functional application!
See also
- See the complete example on GitHub and deploy it to Vercel
- Build a Twitter Clone with the Next.js App Router and Supabase - free egghead course
- Explore the pre-built Auth UI for React
- Explore the Auth Helpers for Next.js
- Explore the Supabase Cache Helpers
- See the Next.js Subscription Payments Starter template on GitHub